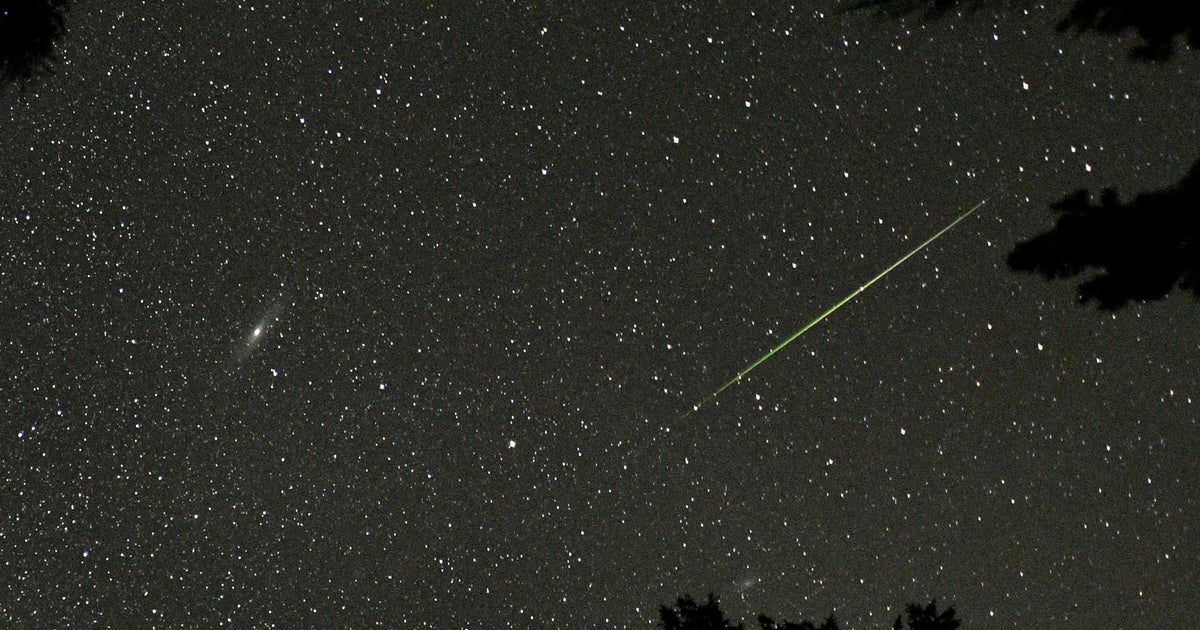
(CNN) – January kicks off with the Quadrantids, one of the fastest however strongest meteor showers of the year.
The shower is expected to peak overnight between January 3 and 4, in accordance to the American Meteor Society. Sky-gazers in the Northern Hemisphere can most effective see the shower between the late-night several hours of Wednesday and dawn on Thursday.
Meteors are leftover items from broken asteroids and comet particles that unfold out in dusty trails orbiting the sun. Each year, Earth passes by means of the debris trails, and parts of dust and rock create colourful, fiery displays identified as meteor showers as they disintegrate in Earth’s atmosphere.
The Quadrantid shower is notoriously really hard to notice owing to its quick peak of six hrs. The peak has a constrained period in comparison with most meteor showers, which peak in excess of two days, since the shower only has a skinny stream of particles and Earth passes by the densest focus of all those particles immediately at a perpendicular angle, according to NASA.
Predictions for the shower’s peak variety from 4 a.m. to 10 a.m., but meteors will be visible for hours beforehand. The American Meteor Culture endorses retaining an eye out for meteors from 1 a.m. to 5 a.m.
The earlier time favors individuals along North America’s East Coastline and the afterwards time is far more favorable for observers in Hawaii and Alaska. The Quadrantids generally aren’t seen in the Southern Hemisphere simply because the shower’s radiant point doesn’t increase that high in its sky just before dawn.
What you will see
The peak can incorporate more than 100 visible meteors for every hour. You might even glimpse some fireballs in the course of the meteor shower, which are brilliant blasts of light-weight and shade affiliated with bigger particles that linger longer than usual meteor streaks, according to NASA.
Continue to keep an eye on the north-to-northeastern sky. Stand or sit with the moon at your again from 2 a.m. onward and perspective the skies for at least an hour, the American Meteor Culture advises.
Visibility will count on any wintry inclement weather conditions in the Northern Hemisphere. And the moon will be about 51% full, which may impression the visibility of the shower, but the modern society suggests attempting to block the moon with a tree or developing.
If you are living in an urban spot, you may possibly want to generate to a put that isn’t complete of shiny city lights. If you’re equipped to uncover an spot unaffected by light pollution, meteors could be seen every pair of minutes from late evening right until dawn.
Uncover an open up place with a vast perspective of the sky. Make sure you have a chair or blanket so you can look straight up. And give your eyes about 20 to 30 minutes to regulate to the darkness – without having searching at your phone – so the meteors will be much easier to spot.
Strange origins
If the meteor shower’s name appears odd, it really is almost certainly simply because it does not audio as if it truly is similar to a constellation. Which is because the Quadrantids’ namesake constellation no for a longer time exists – at least, not as a recognized constellation.
The constellation Quadrans Muralis, very first noticed and noted in 1795 in between Boötes and Draco, is no longer bundled in the Global Astronomical Union’s checklist of modern day constellations simply because it really is viewed as obsolete and isn’t really applied as a landmark for celestial navigation any longer, in accordance to EarthSky.
Like the Geminid meteor shower, the Quadrantids occur from a mysterious asteroid or “rock comet,” somewhat than an icy comet, which is unusual. This individual asteroid is 2003 EH1, which usually takes 5.52 decades to entire one orbit around the sunshine and actions 2 miles (3.2 kilometers) across.
But astronomers imagine a next item, Comet 96P/Machholz, might add to the shower, in accordance to EarthSky. The comet orbits the sun each individual 5.3 years.
Scientists believe a much larger comet was gravitationally certain into a shorter orbit by the sunshine close to 2000 BC. The comet still left guiding meteors for decades right before breaking aside someday amongst the many years 100 and 950. As a consequence, the comet still left powering quite a few celestial offspring regarded collectively as the Machholz Complicated, which involves the Quadrantid meteor shower’s mother or father bodies Comet 96P/Machholz and asteroid 2003 EH1 as properly as two unique comet teams and eight meteor showers, in accordance to EarthSky.
Meteor showers of 2024
After the Quadrantids, there is a little bit of a lull in meteor shower activity, and the subsequent a single will not likely happen right until April.
Lyrids: April 21-22
Eta Aquariids: May perhaps 4-5
Southern delta Aquariids: July 29-30
Alpha Capricornids: July 30-31
Perseids: August 11-12
Draconids: October 7-8
Orionids: October 20-21
Southern Taurids: November 4-5
Northern Taurids: November 11-12
Leonids: November 17-18
Geminids: December 13-14
Ursids: December 21-22