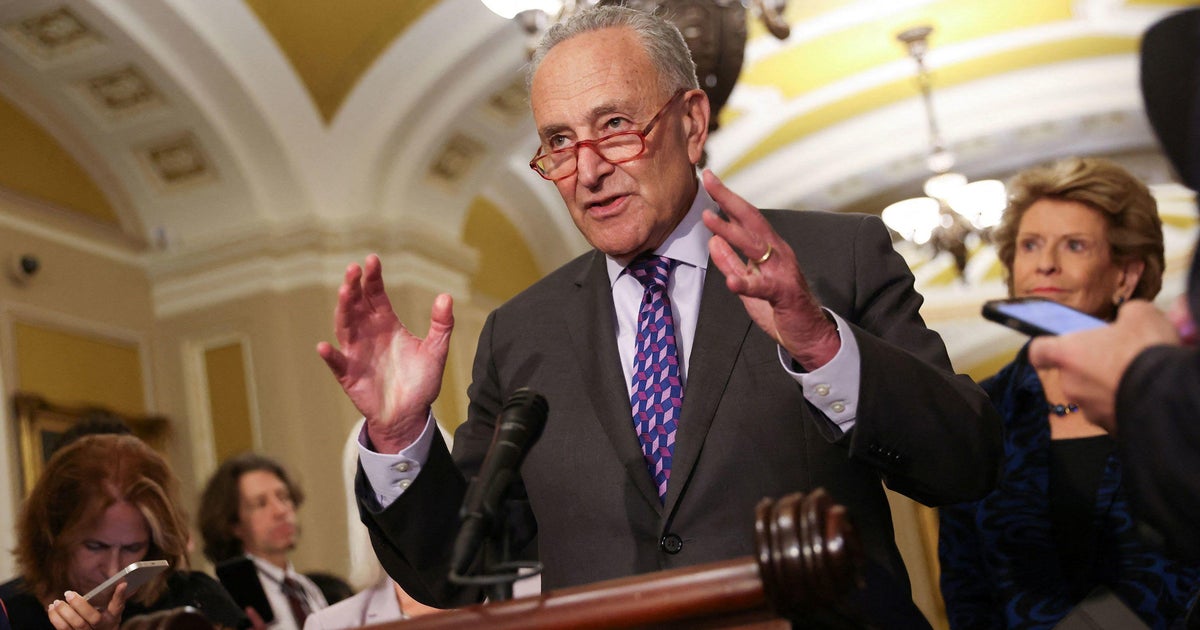
WASHINGTON — Some of the most influential voices in the tech market are meeting with federal lawmakers Wednesday as the US Senate prepares to attract up legislation regulating the quickly-moving artificial intelligence marketplace.
Between those people attending the in-human being party are the CEOs of Anthropic, Google, IBM, Meta, Microsoft, Nvidia, OpenAI, Palantir and X, the company previously recognized as Twitter. The guest checklist also features Bill Gates, the former CEO of Microsoft, and Eric Schmidt, the former CEO of Google, along with top officers from the leisure marketplace, civil rights groups and labor corporations.
Today’s assembly and its anticipated all-star cast marks the first of 9 classes hosted by Senate Greater part Chief Chuck Schumer, who has pledged to craft complete guardrails regulating the AI sector in what he is explained as an unparalleled congressional energy.
“With AI we are not able to be like ostriches sticking our heads in the sand,” Schumer claimed, in accordance to well prepared remarks obtained by CNN. He also noted this is, “a dialogue never ever prior to viewed in Congress.”
The push displays policymakers’ growing consciousness of how artificial intelligence, and specially the type of generative AI popularized by equipment this kind of as ChatGPT, could most likely disrupt small business and day to day lifestyle in various strategies — ranging from rising professional productiveness to threatening work opportunities, countrywide stability and intellectual assets.
The session at the US Capitol in Washington could give the tech field its most major option yet to affect how lawmakers design and style the rules that could govern AI. Some corporations, such as Google, IBM, Microsoft and OpenAI, have previously presented their individual in-depth proposals in white papers and blog site posts that describe levels of oversight, testing and transparency — though some companies differ on important issues this sort of as whether or not a new federal company is necessary to control AI. (It will also likely be the very first time that Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg and X owner Elon Musk have shared a place considering that the two adult males started difficult each and every other to a cage battle months in the past.)
But crucially, the party could also shed light-weight on the political feasibility of a wide, sweeping AI law, placing anticipations for what Congress could attain.
“I consider what these message boards will do is give some perception into, you know, what is the array of viewpoint amid members of Congress?” claimed Christopher Padilla, vice president of IBM’s international government affairs group. “Is there some consensus on some primary matters, like transparency, or respecting mental assets policies, or explainability of algorithms? Is there a prevalent denominator someplace in which ample customers could agree? I believe we’ll learn that by this procedure.”
At the assembly, Padilla extra, IBM programs to spotlight how some of the company’s clients are at the moment making use of its AI applications, as very well as IBM’s proposed eyesight for AI plan, which phone calls for making use of escalating limitations to algorithms dependent on the challenges their use may possibly cause. IBM CEO Arvind Krishna will also look for to “demystify” a broadly held perception that AI progress is done only by a handful of providers like OpenAI or Google, Padilla said.
Connect with for regulation
Executives this kind of as OpenAI CEO Sam Altman by now wowed some senators by publicly calling for new procedures early in the industry’s lifecycle, which some lawmakers see as a welcome contrast to the social media sector that has resisted regulation.
Clement Delangue, co-founder and CEO of the AI firm Hugging Deal with, tweeted final thirty day period that Schumer’s guest list “could possibly not be the most representative and inclusive,” but that he would “test my very best to share insights from a wide range of local community users, specially on subject areas of openness, transparency, inclusiveness and distribution of electricity.”
Civil society teams have voiced problems about AI’s doable hazards, these as the hazard that badly qualified algorithms may inadvertently discriminate in opposition to minorities, or that they could ingest the copyrighted is effective of writers and artists without having payment or permission. Some authors have sued OpenAI about those claims, although many others have asked in an open up letter to be paid out by AI companies. News publishers this kind of as CNN, The New York Instances and Disney are some of the articles producers who have blocked ChatGPT from working with their written content. (OpenAI has stated exemptions this sort of as honest use implement to its instruction of massive language products.)
“We will press challenging to make absolutely sure it’s a definitely democratic approach with entire voice and transparency and accountability and balance,” explained Maya Wiley, president and CEO of the Management Conference on Civil and Human Rights, “and that we get to one thing that essentially supports democracy supports financial mobility supports instruction and innovates in all the best strategies and ensures that this safeguards individuals and folks at the front end — and just not test to fix it following they’ve been harmed.”
The problems mirror what Wiley described as “a elementary disagreement” with tech providers extending from how social media platforms have managed mis- and disinformation, dislike speech and incitement.
“They’re sophisticated troubles, but their way of how [the companies] understand and balance them, how they see price centers in trust and protection instead than as genuinely significant investments …. we have authentic disagreements there,” Wiley mentioned, incorporating that offering underrepresented groups a seat at the table will be critical to a effective result. “Though we share a large amount of the exact principles in many instances, I consider the dilemma is, how do we uncover the ideal harmony that understands there are some authentic issues on all sides of this discussion, but that with out representation, with no entry … we are likely to have larger sized societal troubles.”
Building policy
Navigating these diverse passions will be Schumer, who alongside with a few other senators — South Dakota Republican Sen. Mike Rounds, New Mexico Democratic Sen. Martin Heinrich and Indiana Republican Sen. Todd Young — is primary the Senate’s tactic to AI. Earlier this summer time, Schumer held 3 informational sessions for senators to get up to pace on the technologies, which includes one labeled briefing showcasing shows by US national stability officials.
Wednesday’s assembly with tech executives and nonprofits marks the subsequent stage of lawmakers’ education on the challenge right before they get to work building plan proposals. In saying the collection in June, Schumer emphasized the will need for a very careful, deliberate approach and acknowledged that “in numerous strategies, we’re setting up from scratch.”
Schumer’s personal involvement in the exertion highlights what he has explained as the exceptional problem that AI poses for congressional leaders, and the want for a exclusive process.
“AI is compared with everything Congress has dealt with before,” he mentioned. “It’s not like labor, or healthcare, or protection, exactly where Congress has experienced a long record we can function off of. Professionals aren’t even guaranteed which issues policymakers should be asking.”
In a proposed framework for laws, Schumer proposed that any guidelines Congress passes to control AI must prioritize innovation though making certain that democracy, national security and consumers’ capacity to have an understanding of the technological innovation are not compromised. A smattering of AI payments have already emerged on Capitol Hill and seek out to rein in the marketplace in different means, but Schumer’s press represents a bigger-amount exertion to coordinate Congress’s legislative agenda on the difficulty.
New AI legislation could also provide as a potential backstop to voluntary commitments that some AI firms designed to the Biden administration earlier this yr to make certain their AI designs endure outside screening before they are produced to the community.
But even as US lawmakers prepare to legislate by meeting with sector and civil culture groups, they are now months if not yrs driving the European Union, which is envisioned to finalize a sweeping AI legislation by year’s end that could ban the use of AI for predictive policing and restrict how it can be made use of in other contexts.