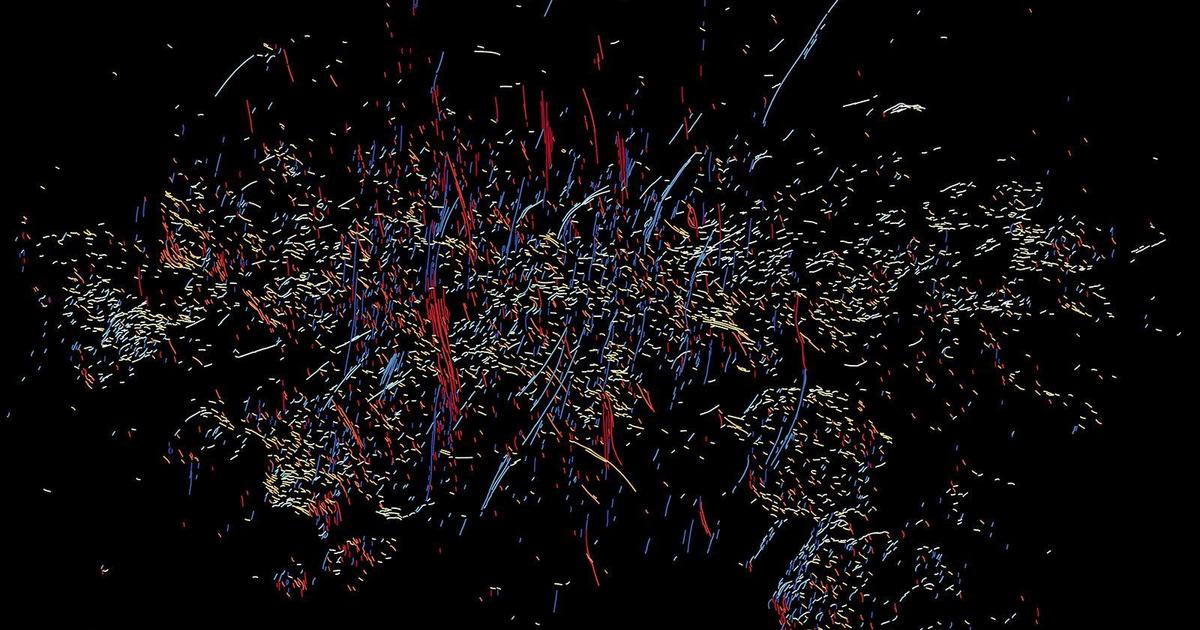
MIAMI — An worldwide workforce of astrophysicists has found hundreds of mysterious constructions in the centre of the Milky Way galaxy.
These one particular-dimensional cosmic threads are hundreds of horizontal or radial filaments — slender, elongated bodies of luminous fuel that potentially originated a few million a long time in the past when outflow from Sagittarius A*, the Milky Way’s central supermassive black gap, interacted with bordering elements, according to a analyze published Friday in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. The filaments are somewhat short in size, just about every measuring 5 to 10 gentle-decades.
The conclusions arrive virtually 40 decades right after Farhad Yusef-Zadeh, the study’s guide creator, and other researchers discovered a further population of practically 1,000 a person-dimensional filaments, which are vertical and significantly larger sized at up to 150 gentle-decades extensive just about every, in close proximity to the galaxy’s middle. Yusef-Zadeh and collaborators also observed hundreds much more paired and clustered vertical filaments in the exact same location in 2022, acknowledging the filaments ended up most likely linked to Sagittarius A* activity somewhat than bursts of supernovae, which they had formerly thought. The new examine both reinforces and builds upon the earlier findings.
Getting the “new inhabitants of structures that appear to be to be pointing in the route of the black gap” was a surprise, Yusef-Zadeh, a professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern University’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, explained in a news release.
“I was basically surprised when I saw these. We experienced to do a lot of work to create that we weren’t fooling ourselves,” extra Yusef-Zadeh, who’s also a member of the Middle for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics. “We observed that these filaments are not random but show up to be tied to the outflow of our black hole. … It is fulfilling when just one finds get in (the) center of a chaotic discipline of the nucleus of our galaxy.”
The findings similar to the black gap found about 26,000 gentle-years from Earth are “definitely remarkable” and “exhibit how beautiful the universe is,” reported Erika Hamden, an assistant professor of astronomy at the University of Arizona who was not concerned in the review.
Sagittarius A* “is the closest supermassive black gap to us, but it is comparatively tranquil and for that reason fairly challenging to actually research,” Hamden additional. “But this do the job provides evidence that it was just lately ejecting pretty a ton of electricity into room in the type of a jet and conical outflow.”
Finding out far more about the Milky Way
The scientists identified the constructions by examining visuals generated by the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory’s MeerKAT telescope, which has 64 satellite dishes that are each and every 65 toes (nearly 20 meters) tall and connected across 5 miles (about 8 kilometers) of a sparsely populated place with negligible interference.
“The new MeerKAT observations have been a video game changer,” Yusef-Zadeh claimed. “It can be really a specialized accomplishment from radio astronomers.”
Despite the similarities between the recently discovered filaments and individuals discovered in 1984, the authors of the new study never believe the populations share just the exact qualities.
The vertical filaments are located perpendicular to the galactic airplane, even though the horizontal ones are parallel to the aircraft and level radially towards the black hole, according to the information launch. The vertical filaments surround the nucleus of the Milky Way, but the horizontal types appear to distribute out to one facet toward the black gap.
“The distribution and alignment of the filaments can assist demonstrate how the materials has moved and distorted in the previous,” Hamden explained.
Their behavior also differs: The horizontal filaments emit thermal radiation and product linked with molecular clouds partially or fully embedded in the outflow from the black gap, the authors wrote. Molecular clouds consist of gas, dust and stars. The vertical filaments, on the other hand, are magnetic and hold cosmic ray electrons moving nearly as fast as the pace of mild.
The authors feel further more researching the newfound filaments could assistance them “find out much more about the black hole’s spin and accretion disk orientation,” Yusef-Zadeh claimed.
A black hole’s accretion disk is the slender, very hot structure ensuing from materials from a nearby star staying pulled into a circle close to the black gap.
Comply with-up is also necessary to determine regardless of whether the jet-driven outflow from the black gap, and thus extra filaments, show up on the two sides of the black gap, Hamden stated. A jet in this context is a beam of matter ejected from some astronomical objects.
A black hole “normally ejects jets symmetrically … so there ought to be a pair,” Hamden included. “One way to validate that the (filament) construction is established by a little something like a jet is to obtain the two sides of it.”
This would increase “to the complex, energetic image of our individual Milky Way,” she said.
Yusef-Zadeh explained he believes their get the job done is “under no circumstances total.”
“We normally need to make new observations,” he reported, “and continually obstacle our concepts and tighten up our analysis.”